Extended Range Electric Vehicle (EREV) helps to reduce charging inconvenience and revolutionize long-distance driving | |||
 7,254 7,254  0 0  0 0 | |||
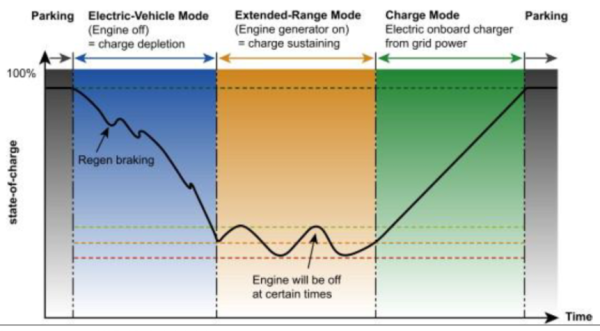
| EREV (Extended-Range Electric Vehicle) refers to a vehicle that obtains power by driving a motor based on electricity generated through an internal combustion engine. The vehicle structure is similar to the plug-in hybrid (PHEV), which consists of an internal combustion engine, a PE system (drive motor), and a battery. However, the internal combustion engine does not intervene in the driving of the vehicle only in the role of a generator (Range Extender) that generates electricity, and the power source supplies the electricity generated by the engine only through the PE system. Therefore, it seems reasonable to view EREV as an electric vehicle (EV) rather than a hybrid vehicle. * The 'hybrid system' uses a combination of engine and PE system power to drive the vehicle
EREV is an alternative technology that compensates for the shortcomings of HEV and BEV, and the development movement of finished car makers is reigniting. EREV was already launched by global automakers such as GM's Chevrolet "Volt" in the early 2010s, but it is a light/small-oriented model rather than a volume model, and sales performance was limited because demand for electric vehicles was not high at the time of launch.
However, recently, EREV is in full swing, focusing on Chinese automakers such as Li Auto, Nio, and Xiaomi, and Japanese automakers such as Nissan (Note e-Power) and Mazda (MX-30), as well as US OEMs such as Stellantis "RAMCHARGER" are also developing and launching EREV. Starting with the launch of 'Li One', an EREV SUV model in 2019, Li Auto sold 380,000 EREVs in 2023 by sequentially releasing L9, L8, and L7.
According to the media, domestic companies such as Hyundai Motor Group and KG Mobility are also believed to be conducting EREV-related R&D recently. The utility of EREV includes 1) reducing the price burden of electric vehicles, 2) eliminating charging infrastructure constraints, and 3) continuing internal combustion engines (to secure eco-friendliness). In the recent slowdown in BEV demand, it is advantageous to respond to eco-friendliness due to high fuel efficiency compared to hybrid, and it is possible to improve driving distance by 50-60% with battery capacity equal to BEV, making it easy to reduce EV costs by reducing battery weight. In the case of Stellantis' RAMCHARGER, despite being a large pickup truck with a tolerance weight of 2.7 tons, it can expand the driving distance to more than 1,000 kilometers while the battery is fully charged and the fuel tank is full with only 92kwh battery (Li-ion) capacity. In the case of the "RAM 1500 REV," a BEV model on the same platform, a driving distance of 500 miles (about 800 kilometers) can be secured by applying a 229kwh battery capacity.
The Li Auto L7 has a battery (Li-ion) capacity of 42.8 kwh and can drive 1,315 km (approximately 1,050 km) based on CLTC.
In addition, as electricity is generated and moved through refuelled fuel, it is possible to solve the convenience of using electric vehicles due to the lack of electric vehicle charging infrastructure, and unlike general engines, EREV engines are advantageous in reducing CO2 and heat loss as the rotational speed/load remains constant. Unlike the engine load cycle, which varies depending on vehicle driving conditions/conditions, the EREV engine operates only for the purpose of charging the battery, so it is possible to optimize the revolution/load cycle that minimizes exhaust gas/CO2 emissions according to the engine mechanism. Nissan noted that it is possible to achieve 50% thermal efficiency, which is improved compared to 40% thermal efficiency of conventional gasoline engines, by applying thermal management technology to meet a certain engine speed/load when announcing the second-generation e-Power (EREV system). In the event of the rise of EREV, the coexistence of internal combustion engines and electric parts makers is expected to ease the burden of rapid restructuring in the automobile market. For engine/ICE parts makers, EREV is an electric generator (Range Extender), and as the engine continues, it is expected that engine manufacturers and internal combustion engine-oriented parts manufacturers such as canisters will be able to secure time to prepare for the conversion of electricity. As the main power source of EREV, PE systems (motors, inverters, reducers, etc.) determine vehicle performance/marketability. The importance of the PE system will continue to increase to improve driving distance and maximum speed. However, since the required power may be always generated through the engine, it is possible to implement a driving distance suitable for the user's demand level even with a small battery capacity. Therefore, the increase in battery demand due to the expansion of EREV supply is expected to be limited.
Tags: EREV Extended-Range Electric Vehicle Long Distance Driving PHEV | |||
| |||
| | |||
|
 1922
1922