The main function of a web cache in a web browsercreated at Feb 24, 2024 1,649 1,649 The main function of a web cache in a web browser is to store copies of documents passing through it (such as HTML pages, 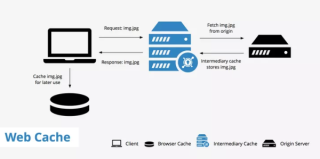 |
The main function of a web cache in a web browsercreated at Feb 24, 2024 1,649 1,649 The main function of a web cache in a web browser is to store copies of documents passing through it (such as HTML pages,  |
The main function of a web cache in a web browser | |||
 1,650 1,650  0 0  0 0 | |||
| The main function of a web cache in a web browser is to store copies of documents passing through it (such as HTML pages, images, and other types of web media) to reduce bandwidth usage, server load, and perceived lag. Here are the key benefits and functions of web caching in browsers:
Speeds Up Web Browsing: By storing local copies of frequently accessed web resources, web caches significantly reduce the time it takes to load a webpage. When a user revisits a webpage, the browser can load content from the cache instead of retrieving it from the internet, resulting in faster page loading times. Reduces Bandwidth Usage: Caching reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted between the client and server. This not only speeds up the browsing experience for the user but also decreases the bandwidth consumption, which is particularly beneficial for users with limited or metered internet connections. Decreases Server Load: By serving content from the cache, browsers reduce the number of requests to the origin server. This helps in distributing the load, especially for popular websites, and can prevent servers from becoming overwhelmed by requests, ensuring smoother operation and availability of web services. Improves Offline Browsing: Some caching mechanisms allow users to access cached content even when they are offline. This can be particularly useful for applications like documentation browsers or for content that the user needs to access regardless of their internet connectivity status. Ensures Content Availability: In instances where the original server is temporarily unavailable or slow to respond, the cache can serve as a backup source for delivering content to the user, albeit potentially slightly outdated, depending on the caching strategy employed. Web browsers typically implement a cache control strategy to determine which resources should be cached, for how long, and when they should be updated. This involves the use of HTTP headers such as Cache-Control, Last-Modified, and ETag to manage the caching behavior efficiently and ensure that users receive up-to-date content without unnecessary delay or bandwidth use. Tags: Cache Web Browser Web Browser Performance Web Cache | |||
| |||
| | |||
|
|