| Securing data, the most important element of generative artificial intelligence (AI) development, is on alert. Until now, AI developers have trained AI models by raking various data online through an automatic program (bot) that is in charge of crawling. Recently, content companies including media companies have banned access to their websites. Previously, AI companies were suing for copyright when using content without permission, but now they are blocking data collection itself.
It is important for big techs to have as much data as possible to learn to improve the performance of AI models, but there are concerns that the amount and quality of data they can use are deteriorating. The Epoch Institute, an American AI research institute, even predicted that if the current trend continues, it will be almost impossible to obtain new AI learning data between 2026 and 2032. It means that learning new data will become increasingly difficult if you do not pay for copyright properly.
Recently, the U.S. cybersecurity company Cloudflare launched a free program that prevents unauthorized data from being taken. It prohibits OpenAI, Google, and Apple from accessing the site without the consent of the website owner. The company said, "It will provide tools to prevent malicious operators from crawling websites on a large scale."
Reddit, the largest online community in the U.S. that uses a lot of AI learning, strengthened anti-crawling tools last month. Reddit signed a contract with Google to provide content to OpenAI for a fee this year, but it is trying to strictly prevent unauthorized crawling of its content.
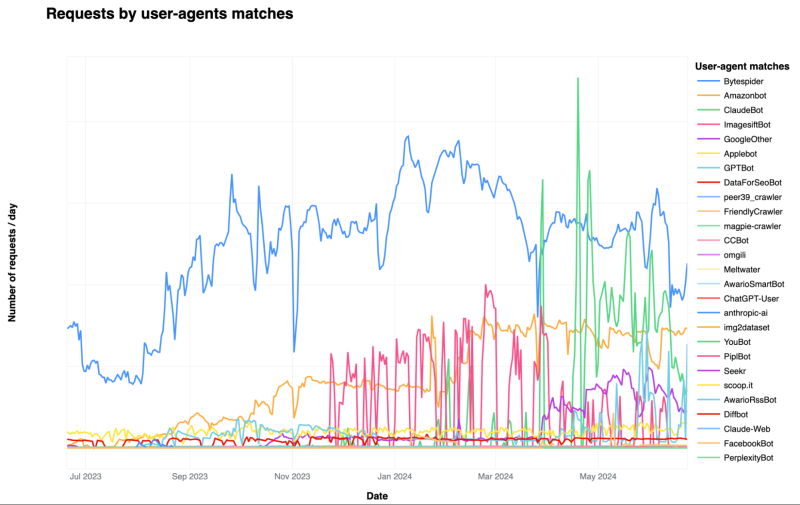
In particular, media companies with high-quality data have already blocked data collection. According to Reuters, 638 out of 1,165 media companies, more than half of them, stopped searching sites for OpenAI, Google, and CommonCrawl, a non-profit data collection organization, as of the end of last year. 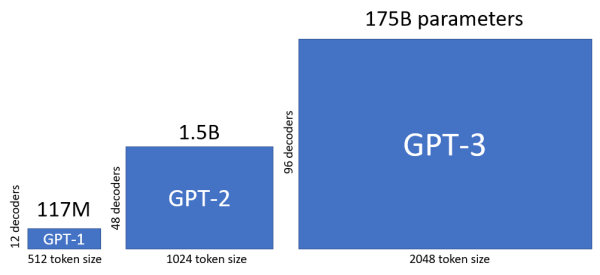
According to the Data Providence Initiative (DPI), a research institute run by MIT, 5 percent of 14,000 websites used to collect AI data blocked "crawler access" last year. In particular, 25 percent of high-quality content such as the media prohibits crawlers. The DPI said, "The number of measures to ban data collection across online websites is increasing rapidly."
With the proliferation of "crawler blocking," AI model developers are having difficulty securing data. Data is continuously emerging online, but it is not enough to keep up with the demand for data needed for AI learning. OpenAI's GPT-3 in 2020 learned about 300 billion tokens (minimum unit of sentence the AI learns). Launched three years later, GPT-4 has trained about 12 trillion tokens, which have increased 40 times. Meta's Generative AI Lama 3 has learned more than 15 trillion tokens this year. According to the Epoch Institute, GPT-5 is expected to learn about 60 trillion tokens, but even with all the high-quality data currently available, it may lack more than 10 to 20 trillion tokens for GPT-5 learning.
The New York Times said, "As media companies, creators, and copyright holders restrict data collection, AI developers who need to constantly secure high-quality data to keep AI models up to date are feeling threatened."
Before the advent of Generative AI, creators did not know how the data obtained by crawling were used. As the Generative AI craze blew, the value of data increased, and as media companies and creators also demanded fair value for it, their reluctance to crawl increased.
In recent years, criticism of AI developers' crawling behavior has been intensifying. This is because it has been revealed that AI developers have still collected data through crawling despite the growing demand for data copyright. According to a recent Business Insider, OpenAI and Antropic have been found to bypass tools that prevent crawling on websites. It has been revealed that PurpleLexity, an AI search startup invested by Amazon and Nvidia, has also collected data by bypassing the IT magazines Wired and Forbes' anti-crawling tools.
Key Takeaways: Data Scarcity and Access Issues in Generative AI Development
- Data is becoming increasingly scarce for AI models: Content companies are actively blocking access to their websites, preventing AI developers from using their content to train models.
- Copyright concerns are driving the shift: Media companies and creators are demanding fair compensation for their content, leading to a reluctance to allow crawling.
- AI developers are facing a data crunch: While data is constantly being generated online, the demand for high-quality data for training powerful AI models is outpacing the supply.
- Data acquisition is becoming more expensive: AI companies are now forced to pay for copyright access, making data acquisition more expensive and potentially limiting the scale of future models.
- Anti-crawling tools are on the rise: Companies like Cloudflare and Reddit are implementing measures to prevent unauthorized data collection, further restricting access.
- Ethical concerns are coming to the forefront: AI developers are facing criticism for bypassing anti-crawling tools and collecting data without proper consent.
- The future of AI development is at stake: The scarcity of high-quality data could significantly impact the development of future AI models, particularly those requiring massive datasets for training.
- The value of data is being recognized: The rise of generative AI has highlighted the importance of data and its economic value, leading to a shift in how data is accessed and used.
Tags: AI Crawling Bots Amazonbot Anti-Crawling Tools Applebot ByteSpider CloudeBot Copyright DPI Data Providence Initiative GPTBot Generative AI GoogleOther ImageshiftBot  
|
 6,802
6,802  0
0  0
0  1922
1922 
