| Global competition to capture the low-orbit satellite market, which is considered a core technology of 6G, is heating up.
Compared to geostationary satellites (300-1500km in altitude), low-orbit satellites (36,000km in altitude) are close to Earth and can expand communication service space beyond the ground network to the sea and air, which is recognized as a 'vascular' of next-generation communication infrastructure.
Until now, "Starlink," a subsidiary of SpaceX's telecommunications company in the U.S., has been considered the leader, but there is no standardized technology worldwide, leading to fierce competition in each country. 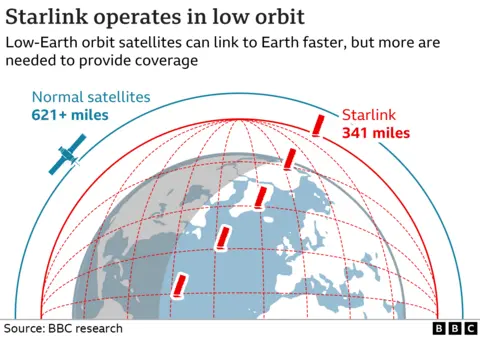
According to Reuters on the 19th (local time), China's state-owned company Shanghai Yuan Xinjiang Science and Technology Corporation (SSST) confirmed that 18 satellites launched from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center on the 5th had successfully settled in a preset orbit.
"This satellite launch marks an important step in terms of China's strategic development," Reuters said. "It is likely to affect the balance of power between countries at war, and competition among countries to occupy low-Earth orbit with great military implications will become fiercer."
Starting this time, a total of 108 satellites will be launched into space this year, and the number will increase to 648 by the end of 2025. China's state-owned Shanghai Yuan Xin Satellite Technology Corporation plans to put a total of 15,000 satellites into orbit by 2030.

The Chinese government-led project is nicknamed "G60 Starlink." It means that it will counter SpaceX's satellite communication network "Starlink." The goal is to complete China's regional communication network using these satellites by 2025 and to enter mobile phone network services by 2030.
Global competition over low-Earth orbit (high altitude of 500-1500 kilometers) satellite communication is intensifying. Low-orbit communication satellites are much closer to Earth than general communication satellites using geostationary orbit (36,000 kilometers), which is advantageous for high-speed communication and has less signal delay.
In addition, it is considered an essential technology in the era of 6G (generation) mobile communication as it enables remote communication that the ground network cannot reach.
It is compared to a "vascular" that connects all parts of our human body as it can provide high-speed Internet to the sea or the air. With the economic feasibility and impact of low-orbit satellite communication growing day by day, China came out as a latecomer to catch the U.S., a leading country.
Elon Musk's space company SpaceX is at the forefront of low-orbit satellite communication. Musk announced the Starlink plan in 2015 and started developing satellites. They saw satellites as the most effective means to distribute the Internet to everyone.
Low-orbit satellites are advantageous for high-speed communication, but due to their low height, there is less scope to connect them. To address this issue, Musk has had thousands of satellite groups take turns sending and receiving signals together.
Since its launch in 2019, SpaceX's Starlink has sent over 6,000 satellites into orbit at an altitude of 550 km. It plans to increase the number of satellites to 42,000 by 2027. Starlink's revenue turned to the black for the first time in November last year.
Under such circumstances, services are being launched to support the advancement of the space business. Amazon Web Service (AWS), which is running a cloud business, is looking for companies that want to enter the space business using its own digital twin technology.
Germany's Livada Space Network also plans to use the AWS cloud to track satellites and launch about 600 satellites by 2025 at an altitude of 1050 kilometers.
Korea has yet to launch a low-orbit communication satellite. It is currently carrying out a research and development project worth about 300 billion won with the aim of 2030. It plans to launch two low-orbit communication satellites to build a pilot network for a low-orbit satellite communication system that includes ground and terminal stations.
Key Takeaways:
- Global competition for low-orbit satellite communication is heating up. This technology is considered a key component of 6G and offers several advantages over traditional communication methods.
- China is aggressively pursuing its own low-orbit satellite network, "Cheon Beomseongjwa," to rival SpaceX's Starlink. China aims to complete its regional network by 2025 and enter the mobile phone market by 2030.
- Low-orbit satellites offer advantages for high-speed communication due to their proximity to Earth. They can also provide communication services to remote areas like the sea and air, making them valuable for diverse applications.
- SpaceX's Starlink is currently the leading player in the low-orbit satellite market. They have launched thousands of satellites and have plans to significantly expand their network in the coming years.
- Other companies, including Amazon Web Services and Livada Space Network, are also entering the low-orbit satellite market. This signifies the growing economic feasibility and impact of this technology.
- South Korea is currently developing its own low-orbit satellite communication system. They plan to launch two satellites by 2030 to establish a pilot network.
Tags: 6G AWS G60 Starlink Livada Space Network Low-Orbit Satellites SSST Shanghai Yuan Xinjiang Science and Technology SpaceX Starlink 千帆星座 천범성좌  
|  6,887
6,887  0
0  0
0  1922
1922 
